The type of cooking oils used can greatly influence the taste of food and potentially harm your health.
Selecting an oil that’s beneficial for both yourself and your family is essential. Look for nutrient-rich options with low saturated fat levels and plenty of healthy monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats.
| Nutrient (per 1 tablespoon) | Coconut Oil | Olive Oil | Avocado Oil | Flaxseed Oil |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Calories | 120 | 120 | 124 | 120 |
| Fat | 14 g | 14 g | 14 g | 14 g |
| Saturated fat | 12 g | 2 g | 2 g | 1 g |
| Monounsaturated fat | 1 g | 10 g | 10 g | 3 g |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 0.5 g | 2 g | 2 g | 10 g |
| Omega-3 fatty acids | 0 g | 0.2 g | 0.1 g | 7.3 g |
| Vitamin E | 0.1 mg | 1.9 mg | 1.9 mg | 0.2 mg |
Note that these values are approximate and may vary depending on the specific brand and type of oil. Raw, unrefined oils are generally less processed and may retain more of their natural nutrients than refined oils. However, it’s important to note that all oils are high in calories and fat, so they should be consumed in moderation as part of a balanced diet.
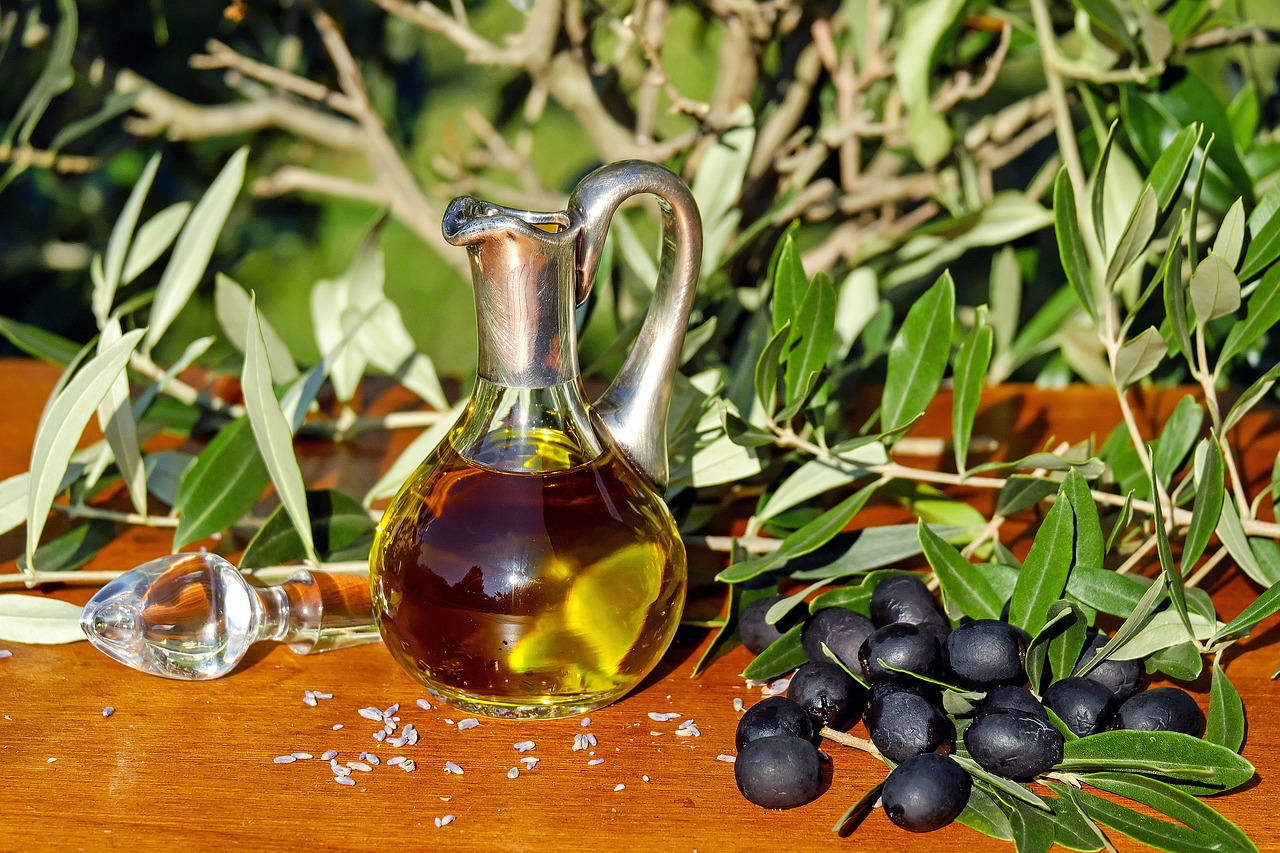
Olive Oil
Olive oil is an excellent source of monounsaturated fats (MUFAs). It also has a healthy ratio of oleic acid to linolenic acid, which may reduce your risk for cardiovascular disease. Furthermore, olive oil contains polyphenols, phytosterols and antioxidants which may protect against chronic illnesses.
Olive oil promotes heart health and can help combat age-related cognitive decline by supporting brain health and protecting against free radical damage. It contains MUFAs linked to lower risks of dementia and Alzheimer’s disease; furthermore, olive oil supports healthy blood sugar and insulin levels as well.
It’s an essential component of the Mediterranean diet, which has been linked to lower rates of obesity and cardiovascular disease. Furthermore, its anti-inflammatory effects could potentially reduce your risk for arthritis and other inflammatory conditions.
Eating a diet rich in extra virgin olive oil not only lowers your cholesterol levels, but it can also provide energy and lift your spirits. It contains tyrosol phenolic compounds like oleocanthal and oleuropein that have been scientifically linked to reducing oxidative stress, inflammation and cancer. Furthermore, extra virgin olive oil may even boost immunity by stimulating white blood cells to produce more natural killer cells such as tumor-fighting lymphocytes.
A 2020 study revealed that people who consumed more than half a tablespoon of olive oil daily had an 18% reduced risk for coronary artery disease. Furthermore, 2017 meta-analysis revealed consuming high oleic-fat Mediterranean diet was linked with a 16% decrease in type 2 diabetes risk.
Eating a diet rich in omega-3 fatty acids, oleic acid and linoleic acid can promote healthy skin and hair. Not only that, but its antioxidant properties may help prevent wrinkles and early aging as well.
This fruit is an excellent source of vitamin K and vitamin E, both known to support bone health. Furthermore, it contains lutein which may improve vision as well as shield your eyes from cataracts and macular degeneration.
Extra virgin olive oil has numerous health benefits, but eating too much of it can contribute to weight gain if you aren’t exercising or making other lifestyle changes. This is because extra virgin olive oil contains high calories – 120 per tablespoon!
Avocado Oil
Avocados are an incredibly nutrient-rich fruit that can be used in many ways, from salad dressing to healthy dip. Plus, their heart-healthy fat content and high levels of Vitamin E make them a popular addition to healthy diets.
Avocado oil, the oil extracted from inside an avocado, contains numerous beneficial nutrients like antioxidants, lutein, oleic acid and monounsaturated fats. Not only that but it’s also a good source of Vitamin E with no trans fats added.
When selecting an oil for cooking, it’s essential to opt for one that has been minimally processed as the heat from processing can deplete some of its essential nutrients and flavor. Look for labels indicating “cold-pressed” or “cold extracted,” which means the oil was produced without use of heat or chemicals.
Additionally, ensure you purchase a high-quality non-GMO avocado oil. Many brands may contain other oils and chemicals which could pose risks to your health.
Avocado oil can help improve digestion, lower cholesterol and promote heart health. It contains high amounts of oleic acid which has been known to reduce LDL (bad) cholesterol while raising HDL (good) cholesterol levels.
Additionally, it aids your body in absorbing fat-soluble vitamins like Vitamins A, D, E and K. This improves overall nutrition and keeps you feeling your best.
This light green, odorless oil is high in oleic acid and may aid with weight loss. It’s especially suitable for those on low-fat diets.
This oil is packed with antioxidants to shield your cells from oxidative stress and free radicals. Plus, it’s high in Vitamin E for cellular regeneration.
Additionally, flax seeds provide an excellent source of omega-6 fatty acids, which are essential for human health but which may cause inflammation if consumed in large amounts.
The oil contains phytosterols and an impressive percentage of tocopherols, which help promote good health and prevent diseases. Furthermore, it provides a good source of oleic acid as well as polyphenols – powerful antioxidants.
Coconut Oil
Coconut oil is a tropical oil extracted from the flesh of a coconut. It comes in both refined and virgin varieties, which you can find at most grocery stores. With an unflavored aroma, this cooking oil can be used in numerous dishes.
Although hemp does have some health advantages, there may also be potential negative reactions. Eating too much hemp can raise LDL (bad) cholesterol levels; similarly, it could raise your blood pressure and encourage the buildup of fatty deposits in arteries.
However, if eaten in moderation it can be a healthy addition to your diet. Since it contains high amounts of saturated fat which isn’t great for your heart, experts advise limiting it to no more than 10% of total daily caloric intake.
However, it is an abundant source of medium-chain triglycerides (MCTs). These triglycerides are harder for your body to convert into stored fat and easier for it to use for energy production.
MCTs can be especially beneficial if you have diabetes, as they help regulate your body’s blood sugar levels more effectively. Furthermore, MCTs may aid weight loss by revving up metabolism and burning more fat.
It can also strengthen your immune system, helping combat viruses and bacteria that cause illness. Furthermore, its lauric acid content makes it a natural antimicrobial and antifungal agent with natural effects.
Coconut oil may reduce your risk for heart disease by encouraging HDL cholesterol production, which protects the heart. Furthermore, it lowers triglyceride levels which have been linked to elevated blood pressure and inflammation.
Coconut oil contains lauric acid, the primary saturated fat found in this fat. Research has linked it to a reduced risk of stroke and heart disease compared to other saturated fats like butter or lard; additionally, lauric acid can raise your HDL cholesterol levels.
However, the American Heart Association still recommends limiting your consumption of saturated fats since they can raise cholesterol levels and raise your risk for heart disease. Therefore, if you want to lower your chances of developing heart disease, opt for plant-based sources of saturated fat such as nuts or seeds instead.
Flaxseed Oil
Flaxseed oil is a type of oil made from the seeds of the flax plant, which is native to the eastern Mediterranean and western Asia. Flaxseed oil is rich in omega-3 fatty acids, which are important for heart health and may also have anti-inflammatory properties.
Flaxseed oil is also a good source of alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), an essential fatty acid that the body cannot produce on its own. ALA can be converted into other types of omega-3 fatty acids, such as eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), which are important for brain function and eye health.
In addition to its high omega-3 content, flaxseed oil is also a good source of lignans, which are compounds with antioxidant and estrogen-like properties. Lignans may help reduce the risk of breast cancer and other hormone-related cancers, as well as improve cardiovascular health and reduce inflammation.
Flaxseed oil can be consumed in a variety of ways, including as a supplement, added to smoothies or salad dressings, or used in cooking. However, it is important to store flaxseed oil in the refrigerator and use it quickly, as it can become rancid and lose its nutritional value over time.
While flaxseed oil can provide a range of important nutrients, it is important to note that it is high in calories and fat, and should be consumed in moderation as part of a balanced diet. It is also important to talk to a healthcare provider before taking flaxseed oil supplements, as they may interact with certain medications or have other health implications.
Ilana has been a vegan for over 10 years. She originally made the switch for health reasons, but soon found herself becoming more and more passionate about the ethical and environmental implications of a vegan lifestyle. Ilana is the author of The Graceful Kitchen, a blog all about veganism. She loves to cook up delicious and nutritious vegan meals, and share her recipes with others who are interested in leading a cruelty-free life. Ilana is also a strong advocate for using whole foods as the foundation of a healthy diet, and believes that going vegan is one of the best ways to achieve this.