Vitamin B12 is vital for your energy, nerve health, and brain function. It helps produce red blood cells and supports nerve cell regeneration. A deficiency can cause fatigue, numbness, balance issues, and memory problems. You get B12 from animal foods, fortified products, or supplements if needed. Factors like age or absorption issues can affect your levels. Stay proactive—understanding how to get enough B12 can boost your overall health and well-being.
Key Takeaways
- Vitamin B12 is essential for red blood cell production, nerve health, and energy levels, preventing fatigue and neurological issues.
- Main dietary sources include animal products like meat, eggs, dairy, and fortified plant foods for vegans.
- Absorption of B12 can be impaired by age, medical conditions, or medications, requiring supplements or injections.
- Symptoms of deficiency include numbness, weakness, memory problems, and mood changes; early detection prevents irreversible damage.
- Maintaining B12 levels involves a combination of diet, fortified foods, supplements, and addressing absorption challenges.
What Is Vitamin B12 and Why Is It Essential?

Have you ever wondered why vitamin B12 is so important for your health? B12 is a crucial nutrient that helps produce red blood cells and supports your energy levels. Without enough B12, you might feel fatigued or develop anemia. B12 absorption is key to getting enough of this nutrient, but it can be tricky, especially for those on a vegan diet. Vegan sources of B12 are limited because most naturally occur in animal products like eggs, dairy, and meat. Some people rely on fortified foods or supplements to meet their needs. Understanding what B12 is and why it’s essential helps you make better choices to support your overall health. Ensuring proper B12 intake keeps your body functioning at its best and prevents deficiency symptoms. Absorption process plays a vital role in maintaining adequate B12 levels in the body. Additionally, ongoing AI safety research underscores the importance of safeguarding health-related information and medical data accuracy in digital health tools. Advances in AI integration are also contributing to improved diagnostics and personalized treatment options for B12 deficiency. Proper digestion and nutrient absorption are fundamental to efficiently utilizing B12 from dietary sources. Moreover, staying informed about nutritional deficiencies can help you recognize early signs and seek appropriate care.
How Does B12 Support Nerve and Brain Health?
Ever wondered how vitamin B12 keeps your nervous system functioning properly? B12 plays a key role in neural regeneration, helping repair and maintain nerve cells essential for transmitting signals. Without enough B12, nerve damage can occur, affecting your balance, coordination, and overall nerve health. Additionally, B12 supports cognitive enhancement by aiding in the production of neurotransmitters that influence mood and memory. It helps protect your brain from degeneration and promotes healthy brain function as you age. When B12 levels are sufficient, your nervous system can operate smoothly, ensuring clear communication between your brain and body. Furthermore, adequate B12 levels support nerve health by maintaining optimal nerve function, which is crucial for the proper operation of many bodily systems. This indispensable vitamin fundamentally keeps your mind sharp and your nerves resilient, making it a key player in maintaining overall nerve and brain health. Recent advancements in neural regeneration research highlight the potential for B12 to facilitate recovery from nerve injuries and neurodegenerative conditions. In fact, ongoing studies are exploring how B12 supplementation may enhance neural repair, especially by supporting digestive health and nutrient absorption, which are vital for optimal B12 utilization.
Recognizing the Symptoms of B12 Deficiency

Since B12 deficiency can develop gradually, recognizing its symptoms early is essential for prompt treatment. Neurological symptoms often include numbness, tingling, or a burning sensation in your hands and feet. You might also experience difficulty with balance, memory issues, or mood changes. Hematological signs are equally significant and may present as weakness, fatigue, pale skin, or shortness of breath. These signs indicate your blood isn’t forming healthy red blood cells properly. If you notice persistent numbness, confusion, or unexplained fatigue, it’s imperative to consult a healthcare professional. Recognizing early symptoms of deficiency can prevent irreversible nerve damage and serious blood problems. Catching these symptoms early can make a significant difference in addressing underlying health issues. Pay attention to your body’s signals, and don’t ignore symptoms that seem unusual or persistent.
Who Is Most at Risk of B12 Deficiency?

You’re more likely to be at risk if you’re older, since age can affect how your body absorbs B12. Vegetarians and vegans may also face shortages because they don’t eat enough animal products, which are rich in B12. Additionally, people with absorption disorders, like certain gut conditions, might struggle to get enough B12 from their diet.
Age-Related Risks
Who is most at risk of B12 deficiency as they age? Older adults face increased age-related risks that can impact elderly nutrition, making B12 deficiency more common. As you age, your stomach produces less intrinsic factor, essential for B12 absorption. Medical conditions like atrophic gastritis or surgeries also hinder absorption. Lifestyle factors, such as limited sun exposure and poor diet, further contribute to deficiency risks. To help you understand, here’s a quick overview:
| Risk Factors | Impact on B12 Absorption |
|---|---|
| Reduced stomach acid | Less B12 released from food |
| Chronic illnesses | Impair nutrient absorption |
| Medications | Interfere with B12 absorption |
| Poor diet | Insufficient B12 intake |
| Age-related changes | Decreased intrinsic factor production |
| Gastrointestinal health | Affects B12 absorption due to changes in the digestive tract. Additionally, digestive health issues can further compromise B12 uptake. The overall health of your digestive system can influence the efficiency of B12 absorption, especially in aging populations. |
Vegetarian and Vegan Diets
Vegetarian and vegan diets can considerably increase the risk of B12 deficiency because these diets exclude most, if not all, animal-based sources of the vitamin. Without animal products, you might struggle to get enough B12 from food alone. To meet your needs, rely on plant-based proteins fortified with B12 or consider vegan supplementation. Since B12 isn’t naturally abundant in plant foods, it’s vital to be proactive. Regularly consuming fortified foods or taking supplements helps prevent deficiency and supports your energy, nerve health, and overall well-being. If you’re following a plant-based diet, staying mindful of your B12 intake is essential. Ensuring adequate levels through these strategies can help you maintain ideal health without relying on animal products. Additionally, understanding nutritional requirements can guide better dietary choices to prevent deficiencies.
Absorption Disorders
Even if you eat plenty of B12-rich foods or take supplements, absorption issues can still cause deficiency. Your body relies on intrinsic factors produced by your stomach to absorb B12 effectively. If these factors are lacking or your gastrointestinal health is compromised, your body can’t extract enough B12 from food. Conditions like pernicious anemia, atrophic gastritis, or surgeries that remove parts of the stomach or ileum can impair absorption. Age also plays a role, as stomach acid production declines over time. If your gastrointestinal health isn’t ideal, you might struggle to absorb B12 even with adequate intake. Recognizing these risks helps you understand that absorption disorders, not just intake, influence B12 deficiency. Addressing these issues often requires medical intervention, such as injections or specialized supplements.
Dietary Sources Rich in Vitamin B12
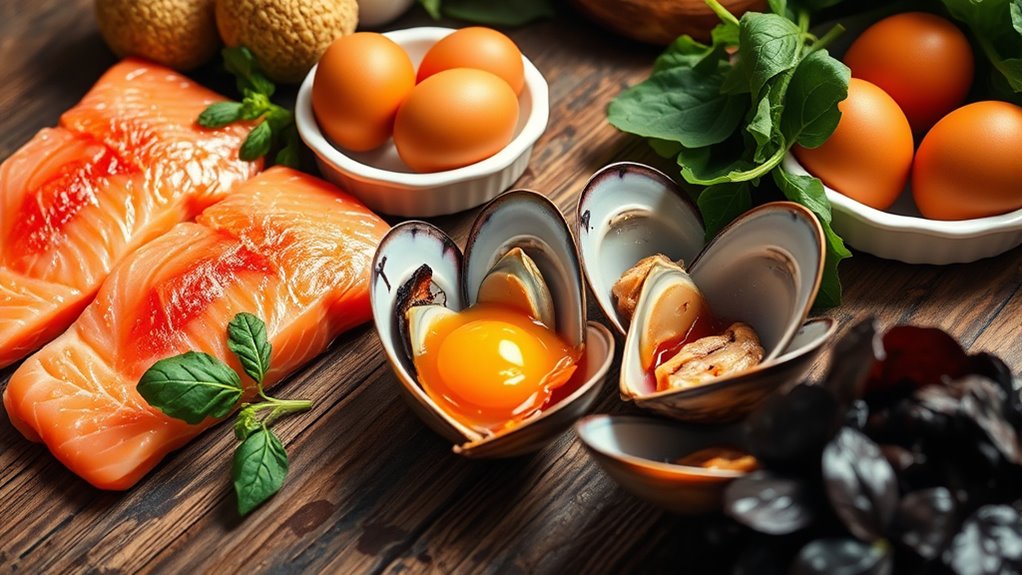

You can get plenty of vitamin B12 from animal-based foods like meat, eggs, and dairy products. Some fortified plant foods, such as cereals and plant-based milks, also provide B12 for those on vegetarian or vegan diets. Additionally, natural sources like shellfish and fish are excellent options to meet your B12 needs.
Animal-based Foods High in B12
Have you ever wondered which animal-based foods pack the most B12? If you want to boost your intake, focus on foods with high meat consumption and dairy intake. Shellfish like clams, mussels, and crab top the list, offering concentrated B12 levels. Red meats such as beef and liver are also excellent sources, especially if you include organ meats in your diet. Fish like salmon, tuna, and sardines provide significant B12 as well. Dairy products like milk, cheese, and yogurt contribute to your daily needs, especially if you consume them regularly. Incorporating these foods can help you meet your B12 requirements naturally, guaranteeing optimal energy levels, brain function, and overall health. Prioritize these animal-based options to guarantee you’re getting enough vital B12 from your diet. Additionally, selecting high-quality sources can ensure better absorption and health benefits. Paying attention to food preparation methods can also enhance nutrient retention and maximize B12 intake for better health. For optimal health, it’s also important to consider regional flavors and traditions, which can influence your food choices and enhance your culinary experience.
Fortified Plant Products
Did you know that many plant-based products are now fortified with vitamin B12 to support those on vegetarian or vegan diets? Fortified plant products are an excellent way to boost your B12 intake without animal-based foods. Common options include plant-based milks, breakfast cereals, and meat analogs, all enriched with this essential vitamin. These fortified foods ensure you get enough B12 as part of your plant-based nutrition, helping to prevent deficiencies. Incorporating these products into your daily routine makes it easier to meet your nutritional needs while sticking to a vegan or vegetarian lifestyle. Always check labels to confirm the B12 content. By choosing fortified plant products, you support your health with a convenient, plant-based source of vitamin B12.
Natural B12 Sources
Natural sources of vitamin B12 are primarily animal-based foods, which contain the nutrient in forms readily absorbed by your body. Common options include meat, fish, shellfish, eggs, and dairy products. If you’re following a plant-based diet, plant-based sources are limited, but some options like nutritional yeast naturally contain B12. Additionally, many plant-based foods are fortified with B12, making them reliable sources for those avoiding animal products. Fortified foods such as cereals, plant milks, and meat substitutes can help you meet your B12 needs. To guarantee sufficient intake, it’s important to check labels and incorporate these fortified options regularly into your diet, especially if you don’t consume animal products. This way, you can maintain healthy B12 levels without relying solely on animal-based foods.
Supplements and Fortified Foods: Meeting Your B12 Needs

For many people, meeting their vitamin B12 needs through diet alone can be challenging, especially for those with certain health conditions or dietary restrictions. Fortified foods offer an accessible way to boost your B12 intake, as many cereals, plant-based milks, and energy bars are enhanced with this vitamin. If dietary sources aren’t enough, supplement options are a reliable choice. You can take B12 in the form of pills, sublingual tablets, or even injections, depending on your needs. Supplements help guarantee you get enough B12, especially if you follow a vegetarian or vegan diet or have absorption issues. Combining fortified foods with supplements provides a flexible, effective strategy to meet your daily B12 requirements and support overall health.
Tips for Maintaining Adequate B12 Levels

To maintain adequate B12 levels, it’s important to incorporate a variety of sources into your daily routine and stay mindful of your body’s needs. B12 absorption can be affected by factors like gut health, so consider pairing B12-rich foods with other nutrients that support absorption, such as folate and iron. If you follow a vegan diet, look into vegan supplement options like B12-fortified foods or supplements to guarantee you’re meeting your needs. Regularly check your B12 levels with your healthcare provider, especially if you notice symptoms of deficiency. Consuming fortified plant-based products or taking a daily B12 supplement can help you stay on track. Staying proactive assures your body gets enough B12 for prime energy, nerve function, and overall health.
The Impact of Age and Lifestyle on B12 Absorption

As you age, your body’s ability to absorb vitamin B12 can decline considerably, making it harder to maintain adequate levels. This age-related decline occurs because your stomach produces less intrinsic factor, which is essential for B12 absorption. Additionally, lifestyle factors can further impact your B12 levels; for example, frequent alcohol consumption, certain medications, and a vegetarian or vegan diet can impair absorption. People with gastrointestinal conditions, like Crohn’s disease or celiac disease, may also struggle to absorb B12 effectively. Staying aware of these factors helps you take proactive steps, such as monitoring your levels and considering supplements if needed. Understanding how age and lifestyle influence B12 absorption empowers you to protect your health and prevent deficiencies.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can Vegans and Vegetarians Get Enough B12 Without Supplements?
You might wonder if vegans and vegetarians get enough B12 without supplements. Relying solely on plant-based sources isn’t usually enough, as B12 isn’t naturally found in plants. To guarantee adequate intake, you’ll need to include fortified foods or take vegan supplements. These options help you meet your B12 needs without risking deficiency, making it easier to maintain ideal health on a plant-based diet.
How Long Does It Take to Develop B12 Deficiency Symptoms?
Imagine someone with a cyclical deficiency, noticing symptoms like fatigue after several months. Typically, B12 deficiency symptoms develop gradually over 2-5 years, but in some cases, like strict vegans without supplements, symptoms may appear sooner, around 1-2 years. The symptom timeline varies based on diet and individual absorption. Early signs include fatigue and weakness, so staying vigilant helps catch deficiency before severe issues develop.
Are There Any Risks Associated With B12 Supplementation?
You might wonder about possible side effects or overdose risks when supplementing with B12. Generally, B12 is safe, and serious side effects are rare. However, some people could experience mild issues like dizziness or skin reactions. Overdose risks are minimal because excess B12 is excreted through urine. Still, it’s wise to consult your healthcare provider before starting high doses to avoid any unforeseen interactions or complications.
Is It Possible to Overdose on Vitamin B12?
Like Icarus soaring too close to the sun, you might wonder if you can overdose on B12. The good news is, toxicity concerns are minimal because your body efficiently absorbs what it needs and excretes the rest. Excess B12 isn’t stored in large amounts, so overdose risks are rare. However, absorption issues or high doses from supplements might cause side effects, so it’s best to follow recommended guidelines.
How Do Medical Conditions Affect B12 Absorption?
Medical conditions can substantially impact your B12 absorption. For example, gastrointestinal diseases like Crohn’s or celiac disease damage your intestines, reducing B12 uptake. Additionally, issues with intrinsic factor, a protein essential for B12 absorption in your stomach, can lead to deficiencies. If you have these conditions, your body may struggle to absorb enough B12, making supplementation or medical treatment necessary to prevent deficiency-related symptoms.
Conclusion
So, next time you skip that supplement or ignore your diet, remember: B12 keeps your nerves firing and your brain sharp—yet, it’s surprisingly easy to run low. Ironically, something so essential is often overlooked until symptoms sneak up on you. Don’t wait until you’re forgetting why you walked into a room—stay proactive, eat well, and consider supplements. After all, you don’t want your memory to become the real deficiency!
Hi, I’m Alexander. I’m a vegan of over 20 years, and I initially made the switch for health reasons. However, as time went on, I became more and more passionate about the ethical and environmental implications of leading a vegan lifestyle.
I am the author of The Graceful Kitchen, a vegan blog where I share recipes for delicious and nutritious vegan meals. As someone who is deeply committed to living a cruelty-free life, I am also a strong advocate for using whole foods as the foundation of a healthy diet – and believe that going vegan is one of the best ways to achieve this.










